A motor is mechanically coupled with a load. The mathematical relationship between the mechanical speed ($\omega_m$) and the torque ($T$) is developed in equation (1) where $J$ is the moment of inertia.
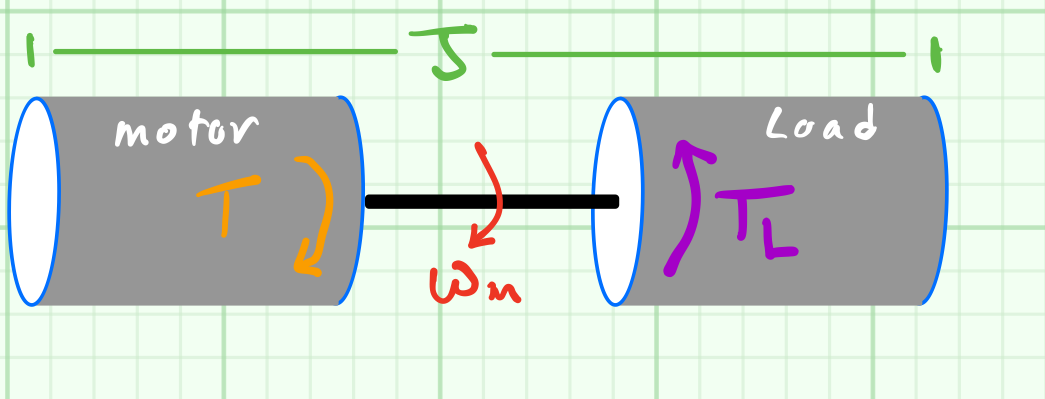
$$\begin{align}T-T_L&=\frac{d}{dt}(J \omega_m) \nonumber\\
T-T_L&= J \frac{d\omega_m}{dt} + \omega_m \frac{dJ}{dt} \nonumber\\
T&= J \frac{d\omega_m}{dt} + T_L
\end{align}$$
In steady-state ($T=TL$) as the speed reached the reference speed and no change in speed is observed.